Research on New Therapeutic Strategies for Alzheimer's Disease by Modulating Autophagy
Lu Jia Hong, Su Huan Xing
University of Macau
The development of drugs for Alzheimer's disease (AD) has been challenging, making it crucial to decipher new molecular pathogenic mechanisms of AD to develop novel treatment strategies. Autophagy is a highly conserved cellular degradation and quality control mechanism that holds significant importance in maintaining neural system homeostasis. This project focuses on the intrinsic connection between autophagy and AD, with the primary research objectives being the exploration of pathogenic mechanisms and the discovery of neuroprotective traditional Chinese medicine monomers. Through a multidisciplinary drug screening platform and cross-species disease models, the study systematically elucidates the prospects of autophagy regulation as a new therapeutic strategy for AD, uncovering and deeply analyzing the relationship between autophagic dysfunction and the molecular mechanisms of AD. It reveals the potential and mechanisms of Chinese medicine-derived autophagy-regulating small molecules for treating AD. The research findings of the project highlight the close relationship between autophagy and AD, providing evidence for regulating autophagy as a new therapeutic strategy for AD. The research results of this project have been published in high-impact journals such as "Nature Biomedical Engineering" and cited by several high-impact journals including Nature.
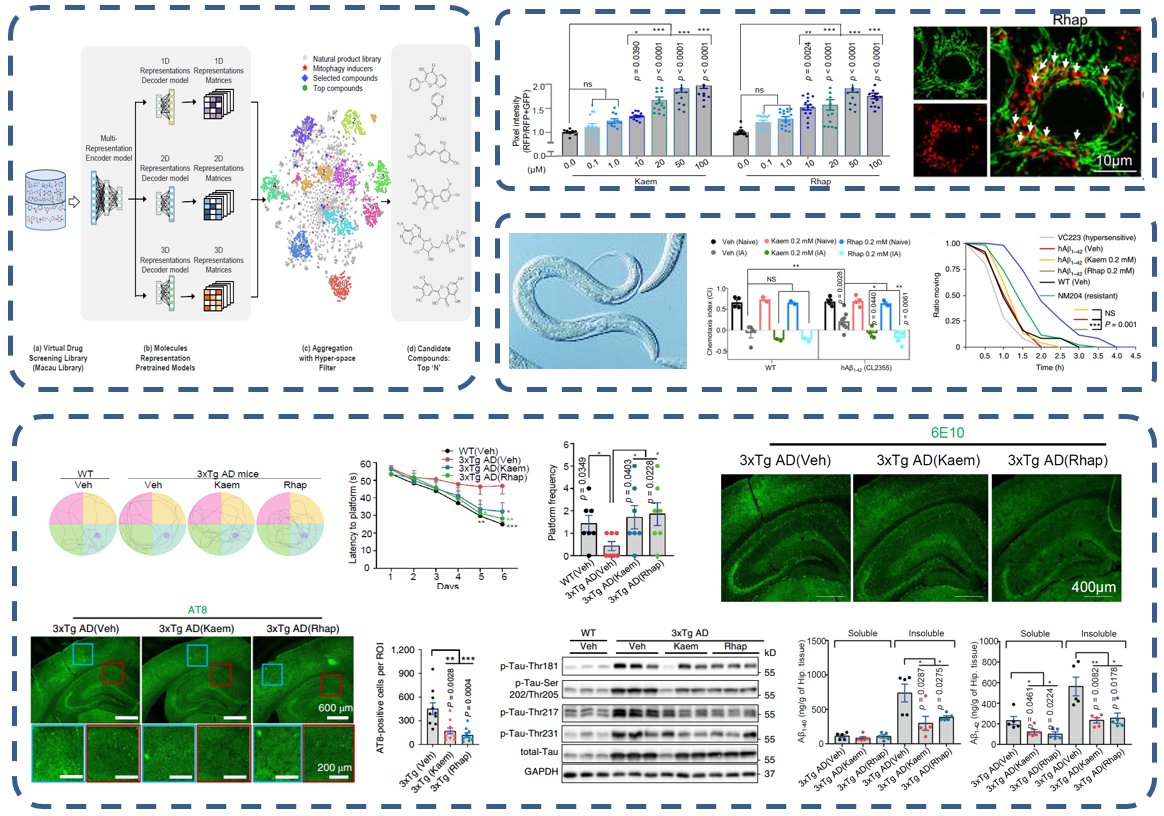
Fig 1 AI screening combined with cross-species model validation revealed mitophagy inducers with therapeutic potential for AD. The figures of representative work“Amelioration of Alzheimer's disease pathology by mitophagy inducers identified via machine learning and a cross-species workflow”published in《Nature Biomedical Engineering》.



